Table of Contents
Overview | Diagnosis | Allergy | Hypersensitivity | Parasites | Anal Gland | Skin Infection | Seborrhea | Immune Mediated | Cancer | Licking | References
Summary:
"If a dog is scratching, licking or chewing the skin, then dog skin itch is probably one of the symptoms. It is also one of the leading reasons for visiting a veterinarian. If itching lasts for more than a week, be sure to visit a vet to rule out any underlying causes such as infection, disease or parasites (fleas, ticks, mange mites). A trip to the vet is required if you smell a bad odor, your dog's behavior has changed such as low energy or the dog is not eating, if any member of your family becomes itchy (could be scabies) or your notice skin sores. Treatment depends on the underlying cause, with oatmeal preparations and other topicals/baths bringing some relief."
Overview
Dog skin itch is a common complaint. It can have many causes so it is sometimes tricky to diagnose and treat the canine skin disorder. Possibilities include:
- Allergies
- Bacterial infection
- Fungal infection
- Skin cancer
- Hypothyroidism
- Fleas
- Endocrine disease (thyroid, pituitary, adrenal)
- Anal gland infection
- Obsessive compulsive licking
Each type of itch has different characteristics that will help in the diagnosis and treatment.
For minor itching you can try the following treatment options to see if there is any improvement:
- Colloidal oatmeal - soothes the skin, particularly when the cause is allergy. Options for dog skin itch include an oatmeal bath, shampoo or topical.
- Tea Tree Oil - Mild antibacterial and anti-fungal treatment.
- Sulfur - Helps with flaking, antibacterial, anti-fungal and relieves itch.
- Salicylic acid - Helps with skin flaking, antibacterial and relieves itch.
- Coal tar - helps with flaking, reduces greasy condition and helps with itch.
- Selenium sulfide - helps with flaking and greasy skin
- Benzoyl Peroxide - Anti-bacterial, unclogs pores, helps with greasy skin. May be drying.
- Chlorhexidine - antibacterial, anti-fungal
- Povidone-iodine - Antibacterial and anti-fungal
- Boric acid - anti-fungal and drying
- Acetic acid - anti-fungal
- Clotrimazole, ketoconazole, miconazole, thiabendaxzole - anti-fungal
- Hemp oil
Herbal Supplements - consider supplements such as Allergy Itch Ease to naturally provide dog itchy skin relief. It contains natural ingredients such as Arum triph which has been used for centuries for skin itch relief. Once you've identified the underlying cause for the itch, you can speed recovery by providing a supportive homeopathic remedy such as PetAlive Skin and Coat Tonic that contains specially selected herbs, nutrients and biochemic tissue salts known to support coat and skin health.
Herbal Skin Topical - if you dog is suffering from itch due to flea bites, consider a topical such as FleaDerm to soothe the skin.
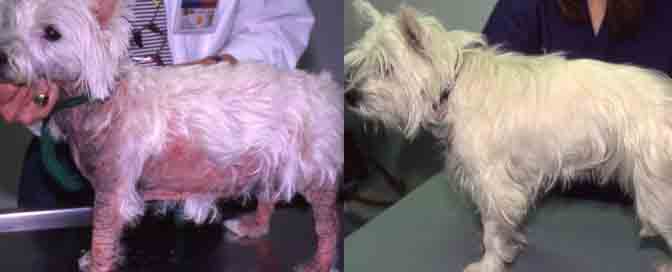
Source: ACVD
Diagnosis
The first step toward diagnosis is to look at where you dog is itching and if you can tell the underlying cause of the itch such as red pimples or raw skin.
Is the skin itch localized (in one area)?
If the itch is only one location, then either a skin parasite such as scabies (mange) or food allergy may be the cause. Food is often the cause if you have made a recent adjustment in your dog's diet. If nothing changed in the diet, try a mange treatment such as Naturasil
Are there multiple skin irritations that see to be symmetric? (patterns that mirror each other)
Causes are often internal such as hypothyroidism, hypoadrenocorticism or pemphigus foliaceus. Allergies may also be the cause.
Multiple skin pimples with no symmetry
Common causes are parasites (fleas, mites)and bacteria. You can try a treatment such as the one indicated above that includes a miticide or anti-flea treatment.
Allergy Related Itch
Symptoms of allergy include licking of the paws, face rubbing, belly licking and ear infections. Allergies usually start early in life and can last throughout the year or start with certain seasons.
Treatment for skin allergy includes a dietary supplement that contains fatty acids, baths with colloidal Oatmeal Shampoo, antihistamine, corticosteroid sprays or allergy shots.
Food Allergy
Symptoms of allergy are paw licking, face rubbing, ear infections. To treat try feeding your dog a simple food that your pet has never eaten before. If the allergy disappears than a food allergy is the cause. It is rare for a dog to have a food allergy. Consider a simple carbohydrate/protein combination or allergen free foods such as Hills z/d.
A natural approach to dog food allergy is to provide a short fast to help reduce stress on the body. Try eliminating your dog's regular diet for 2 to 3 days and replace with a combination of broth and honey or broth and black-strap molasses. If you see improvement, resume the dog's regular diet, but use the "fast" replacement one day per week.
Contact Hypersensitivity
Symptoms happen suddenly and are a reaction to something that has changed in the dogs environment such as bedding or shampoo. Symptoms include itching on the abdomen, feet and chest. Itching can be helped with a colloidal Oatmeal Shampoo, antihistamine or corticosteroid sprays.
Skin Parasite Dog Skin Itch
Itching is caused by an insect that disturbs the skin such as a mite, flea or tick. Review our guide to each type of parasite to determine treatment. Mites (known as Mange or scabies) are best killed with a Miticide such as Naturasil for Mange.
Ear Infection
Primary symptom is scratching of the ears, ear wax and smell. Treatment includes ear drops and ointment. Read more on dog ear infections.
Anal Gland Irritation
Symptoms are scratching of the anus and scratching by dragging the anus along a floor or carpet. Treatment is by draining clogged anus glands. Read more about dog anal glands.
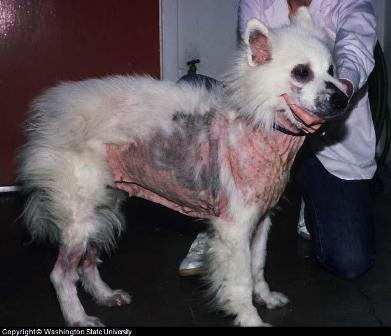
Bacterial Infections that cause Dog Skin Itch
Bacterial skin infection is the second most common type of skin condition after allergy (folliculitis). It occurs when there is infection at the base of the hair follicles. The condition is often misdiagnosed since it tends to be a secondary effect of other skin conditions such as skin allergy and flea allergy.
The disease looks different in each breed with further variation caused by the type of bacteria causing the infection. Papules (a small solid rounded bump rising from the skin that is usually less than 1 centimeter in diameter - less than 3/8 inch across) appear at the base of the hair follicles. Since they burst easily they are often crusted and move from area to area.
You can try DVM Malaseb Medicated Pet Shampoo which is made to combat bacteria.
Seborrhea
This condition is accompanied by dry flaky skin or skin that is greasy to the touch. Symptoms can include itch, thinning hair in patches, scabs, bumps and pimples.
Give your dog frequent baths starting with every other day for 10 days, then 2x a week, then 1x a week depending on the level of improvement you see. If your dog's skin is dry use a cleansing shampoo. These shampoos help address dog dry skin due to environmental factors with a lathering action that helps to remove dirt. A good choice for this purpose is Veterinarian's Best Quick Soothe Hot Spot Foam For Dogs.
If the skin is greasy use a shampoo what contains coal tar, benzoyl peroxide or selenium sulfide (degreaser for the skin) such as Synergy Labs VF Medicated Shampoo.
Use warm water when bathing. Also consider an after bath spray that contains colloidal oatmeal, fatty acids, urea or glycerin.
You may want to consider an a natural skin supplement that contains fatty acids.
Canine Endocrine Disease
There are several types of endocrine disease including diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, Cushing's and Addisons. Symptoms of the disease include hair loss, pimples/lumps, thinning skin, thirst and urinary tract infections.
Treatment Options:
- Medicated baths
- Antibiotics for infection
Immune Mediated Skin Disease
This disease occurs when the immune system attacks its own cells. It starts with lumps on the nose with other symptoms including face sores, ear sores, feet/body sores, scaly skin, toenails that split or break and hair loss.
Treatment for canine immune mediated skin disease includes:
- Corticosteroids
- Antibiotics (for infection if necessary)
- Medicated baths
Canine Skin Cancer
Canine skin cancer can appear in many forms. It includes single or many bumps and sores.Treatment of this condition includes radiation, chemotherapy and surgery.
Obsessive Compulsive Licking
When your dog keeps on licking an area to the point that sores are formed.
Treatment:
- Antibiotics for infection
- Bandages to cover the sore area
- Prescription medication to alter behavior (prozac)
There are also homeopathic remedies that can help reduce nervous anxiety such as Pet Calm.
Have A Question about Your Dog's Skin Condition? Our Team Will Answer It for Free!
Do you have a question or comment? Share it!
Our editors will pick 1 question to answer each week. Please include your dog's age, breed, medical history, medications and if possible, a picture of the condition.
We will do our best to get back to you quickly (it depends on how many questions we receive each day). If you do require an immediate response we suggest using this online dog veterinary service that is available now.
Other Reader Dog Skin Related Questions and Vet Suggestions
Click below to see contributions from other visitors to this page...
Dog with Skin Itch and Hair Loss Not rated yet
I have a 7-month-old Pitbull and Weimaraner mix. He has a skin condition that his dam and siblings all have - dry, flaky, red skin with small bumps. It …
References Dog Skin Itch:
Scott, D. W., Miller, W. H., Griffin, C. E.
Muller and Kirk’s Small Animal Dermatology
Mueller, R. S.
Flea Control in Veterinary Dermatology
ACVD
Brevitz, Betsy
Hound Health Handbook
George Washington University (picture credit)

