Table of Contents
Summary:
"Taking canine blood pressure is becoming routine in many veterinarian offices. Blood pressure is taken with a cuff around the leg or a probe on the skin. Readings are difficult to take. Normal levels of pressure can differ between breeds, so it is not always a straightforward process. Readings that are greater that 180/100 are considered to be high blood pressure or hypertension. If this is the case, your veterinarian will look for the underlying cause of the condition."

Overview:
Dog Blood Pressure is read in two different ways. The first uses a cuff similar to the kind used for humans. It is placed around the dog's leg. The second uses Doppler technology to determine the level of pressure. For this approach, your dog's hair will need to be shaved in the area where a reading is taken.
It is difficult to take an accurate dog blood pressure reading. Unlike humans there are no exact standards for normal levels of blood pressure across breeds. Because of this difficulty and the need for interpretation some veterinarians do not include a blood pressure examination as part of the yearly checkup unless some type of heart or other disease which impacts pressure (renal or kidney failure) is suspected.
The gold standard is an invasive method where a catheter is used. This approach is used for ill patients who are under anesthesia or in intensive care.
When Blood Pressure is Monitored
- Hypertension (renal disease, Cushing's disease, thyroid diseases, diabetes)
- Hypertension (heart murmur, neurological signs, when there is a retinal detachment)
- Congestive heart failure
- When there is a heart murmur
- When a dog is critically ill such as after an injury or when fighting a disease
- After surgery
- Routine screening
- Monitoring during anesthesia
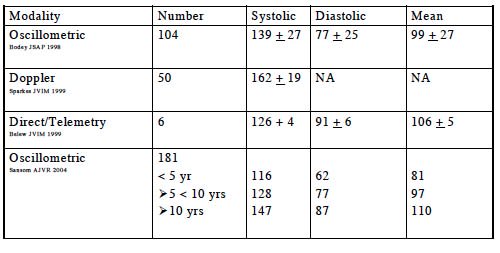
Blood Pressure Range
Blood pressure has two phases called diastole and systole. Blood
pressure measurement is expressed as diastolic, systolic or as a mean
arterial blood pressure. The unit of measurement is mmHg.
In general a normal reading for a dog is systolic pressure of 160-180 mmHG and diastolic pressure around 100 mmHg. Systolic pressure measures one part of the heart cycle when pressure is highest and diastolic measures the other end of the cycle.
Levels that are greater than these are generally considered to be high and indicate a diagnosis of hypertension, another name for high blood pressure.
Source: Dr. De Francesco Terri
Dog Blood Pressure Treatment
Treatment for high blood pressure consists of prescription medication that is similar to the types used in humans such as atenolol.
Natural medicine also has a history of helping dogs with blood
pressure, heart and circulatory needs. Natural ingredients such as
Hawthorne (Crateagus oxycantha), Arnica montana, Kalium phosphate and
Calcium fluoride all are believed to support the heart, circulation and
sustain blood pressure in a normal range. PetAlive
Heart & Circulation is specifically formulated to provide a
natural treatment and prevention option for dog owners. Discuss any
treatment options with your veterinarian so that they can monitor
progress.
